Telegram RAT

Telegram RAT: Technical Architecture, Operational Flow, and Modern Windows Interaction
Introduction to Telegram RAT and Messaging-Based Remote Access Tools
The concept of a Telegram RAT represents a shift in how remote access tools can be architected using existing communication platforms rather than traditional server-based infrastructures. Instead of relying on dedicated command-and-control servers, these tools leverage messaging APIs to establish bidirectional communication channels between the operator and the controlled system.
From a technical perspective, this approach significantly reduces architectural complexity while introducing new design considerations related to message handling, latency, session management, and persistence. Telegram, due to its stable API, global availability, and bot-based automation model, has become a commonly observed medium in this category of remote control frameworks.
Why Telegram Is Used as a Command and Control Channel
Traditional RAT architectures rely on centralized servers, static IP addresses, or web panels, all of which introduce maintenance overhead and potential points of failure. A Telegram-based model replaces these components with a messaging-driven control layer.
From an engineering standpoint, Telegram offers a structured Bot API, event-based message delivery, encrypted transport channels, and cross-network accessibility. In a Telegram RAT design, the messaging platform acts as an intermediary layer, enabling command dispatch and response collection without direct socket exposure.
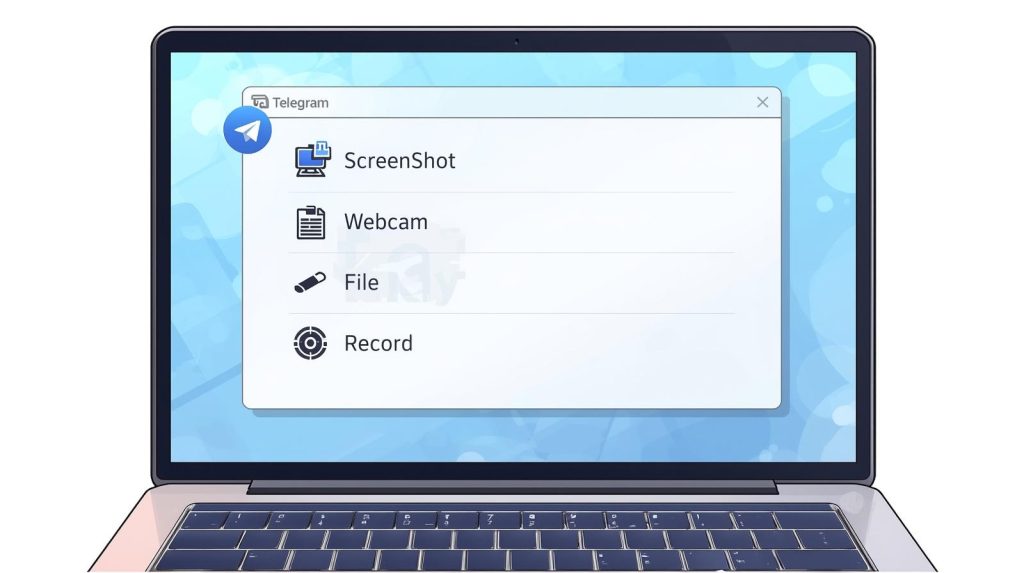
General Architecture of a Python-Based Telegram RAT
Core Control Logic and Message Handling
At the core of the system lies a message processing engine responsible for receiving incoming bot messages, parsing command identifiers, validating execution context, and dispatching commands to internal handlers.
Interaction Between Telegram Bot API and the Client System
The Bot API serves as the communication bridge between the operator interface and the client system. Messages received from Telegram are transformed into structured internal commands, while execution results are serialized and transmitted back through the same channel.
Execution Flow on Windows Operating Systems
Initial Payload Execution Behavior
Upon execution, the application initializes its runtime environment, verifies system compatibility, and establishes a connection context with the messaging API. During this phase, the process typically runs without user-facing indicators.
Silent Background Process Characteristics
Modern Windows environments support multiple background execution contexts. A Telegram RAT leverages these contexts to maintain operational continuity while minimizing resource consumption.
Persistence Mechanisms in Modern Windows Versions
Startup Context Registration
To survive system restarts, the application registers itself within approved startup execution paths, ensuring automatic reinitialization when the operating system boots.
Survivability After System Reboot
This persistence model allows the tool to remain active across reboots while complying with modern Windows execution constraints.

Connection Notification and Session Initialization
Handshake Between Client and Telegram Bot
When the client initializes successfully, it sends a structured notification through the bot interface indicating that the system is online and ready to receive commands.
Session Identification and State Tracking
Each connection session is tracked logically, allowing the operator to distinguish between multiple connected systems.
Command Processing Model
Predefined Command Structures
Commands within a Telegram RAT environment are predefined and mapped to specific internal operations to ensure predictable execution behavior.
Command Dispatch and Response Handling
Once dispatched, commands are executed in controlled system contexts, and results are transmitted back through the Telegram communication channel.
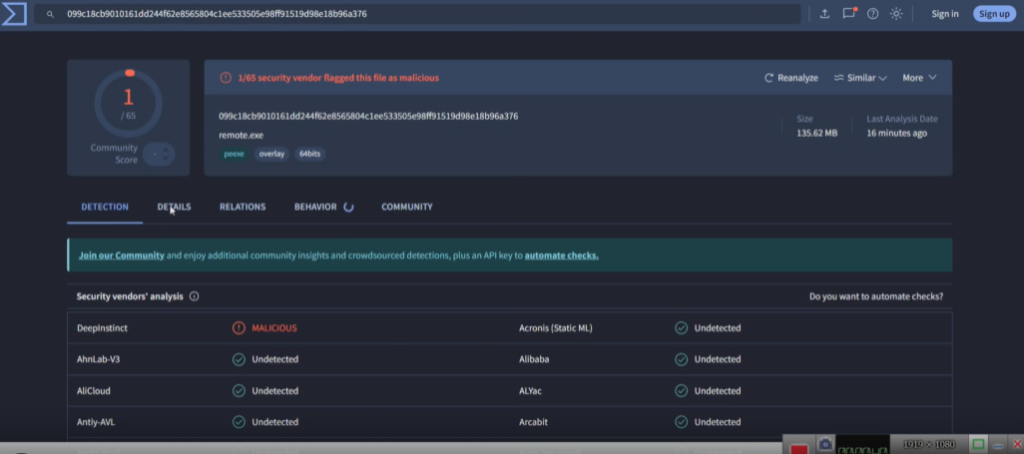
Modular Design Principles
Separation of Core and Feature Modules
The architecture separates communication logic from system interaction modules, improving maintainability and extensibility.
Scalability and Maintainability Considerations
This modular approach allows new capabilities to be added without altering the core communication layer.
Desktop Interaction Capabilities
Remote Desktop Control Concepts
Desktop interaction features operate through abstracted interfaces that interact with the active user session.
User Session Awareness
The RAT adapts its behavior based on the active user context to maintain consistent control logic.
Security Implications of Telegram RAT Usage
Abuse of Legitimate APIs
The use of legitimate messaging APIs complicates traditional detection and filtering mechanisms.
Challenges in Detection
Behavior-based detection plays a critical role in identifying messaging-based remote access tools.
Detection Techniques on Windows Systems
Behavioral Indicators
Indicators include abnormal startup entries, persistent background processes, and unusual messaging activity.
Network and Process-Level Signals
Correlation between process behavior and network communication helps identify suspicious activity.
Limitations and Technical Constraints
Telegram RAT frameworks are subject to API rate limits, message size constraints, and dependency on third-party service availability.
Telegram RAT vs Traditional Server-Based RAT Architectures
Compared to server-based RATs, Telegram RATs reduce infrastructure overhead while introducing platform dependency trade-offs.
Future Trends in Messaging-Based Remote Access Tools
Messaging platforms are increasingly influencing remote management architectures through their APIs.
Legal, Ethical, and Educational Purpose of the DarkFolder Telegram RAT
This tool has been developed by the DarkFolder team strictly for educational, research, and authorized penetration testing purposes. Its primary objective is to support security research and technical learning in controlled environments.
The DarkFolder team states that the tool must only be used on systems with explicit authorization. Any unauthorized or unethical use is strictly prohibited.
The tool is available through the official DarkFolder website and can only be downloaded after full acceptance of the usage terms and ethical guidelines.
Download Telegram RATConclusion
The Telegram RAT model demonstrates how modern messaging platforms can function as decentralized control channels within distributed software architectures. Understanding these mechanisms is essential for both defensive security research and architectural awareness.


2 Comments
how can i buy it?
send mesaage telegram : t.me/DarkFolder_Channel